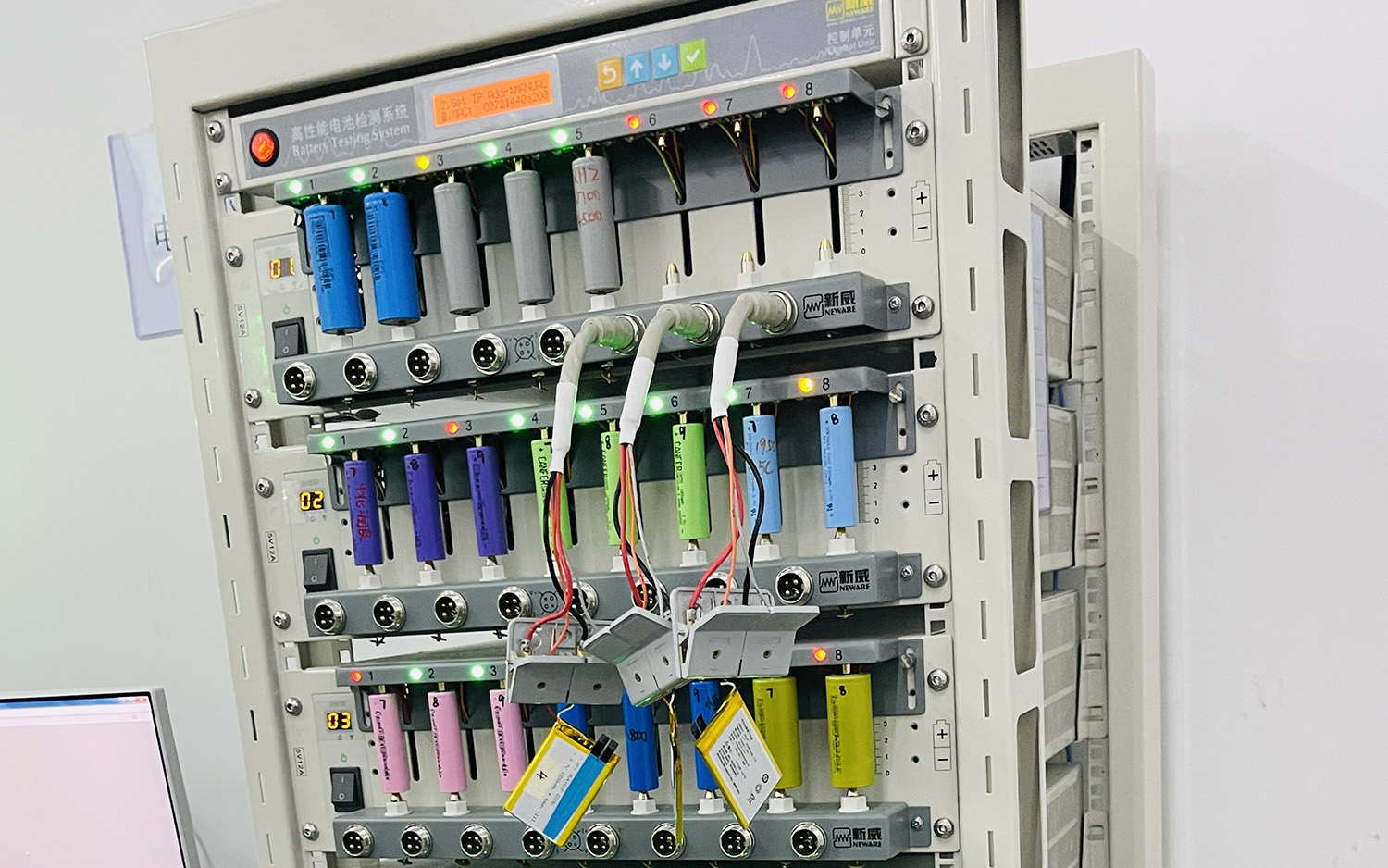
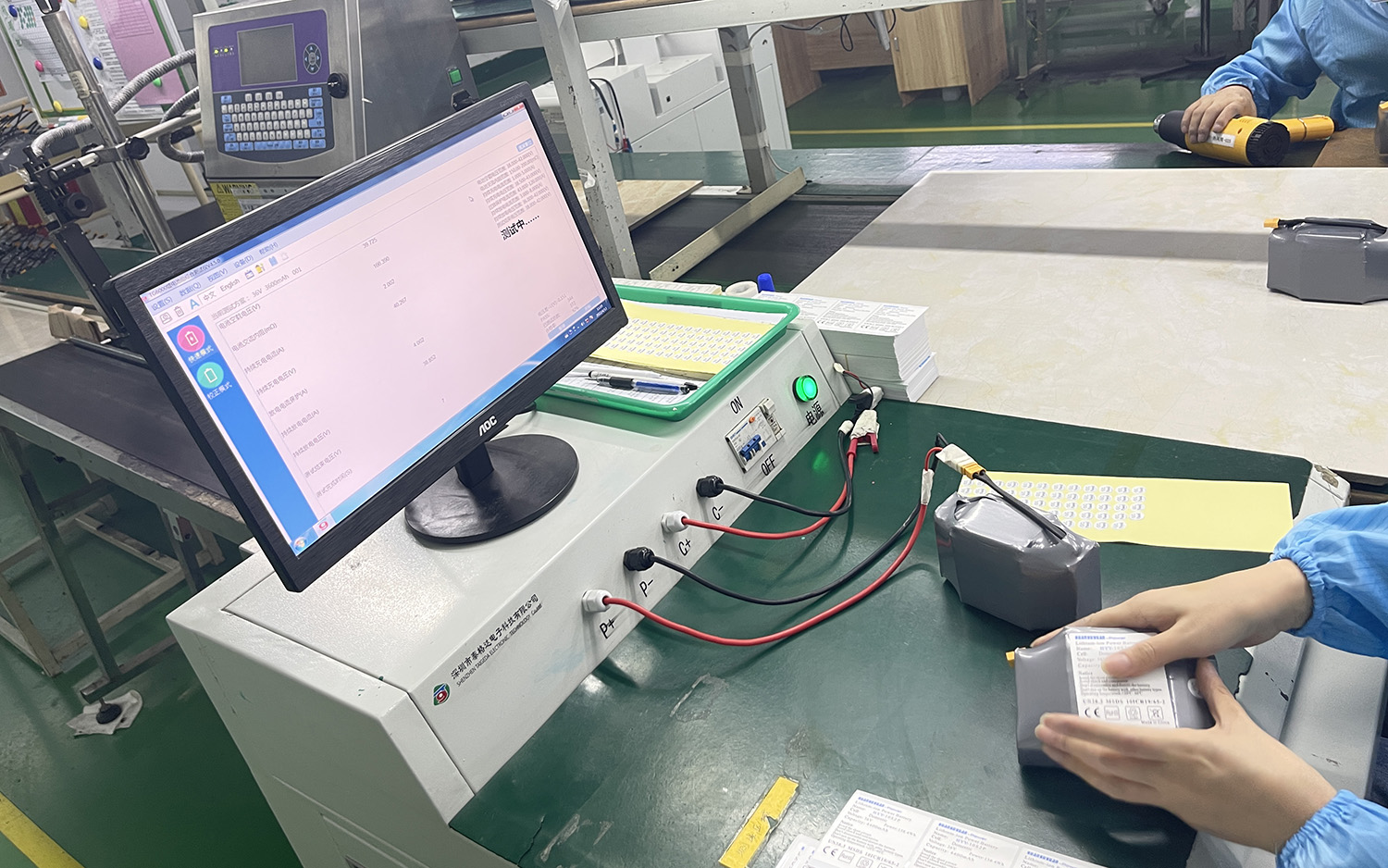
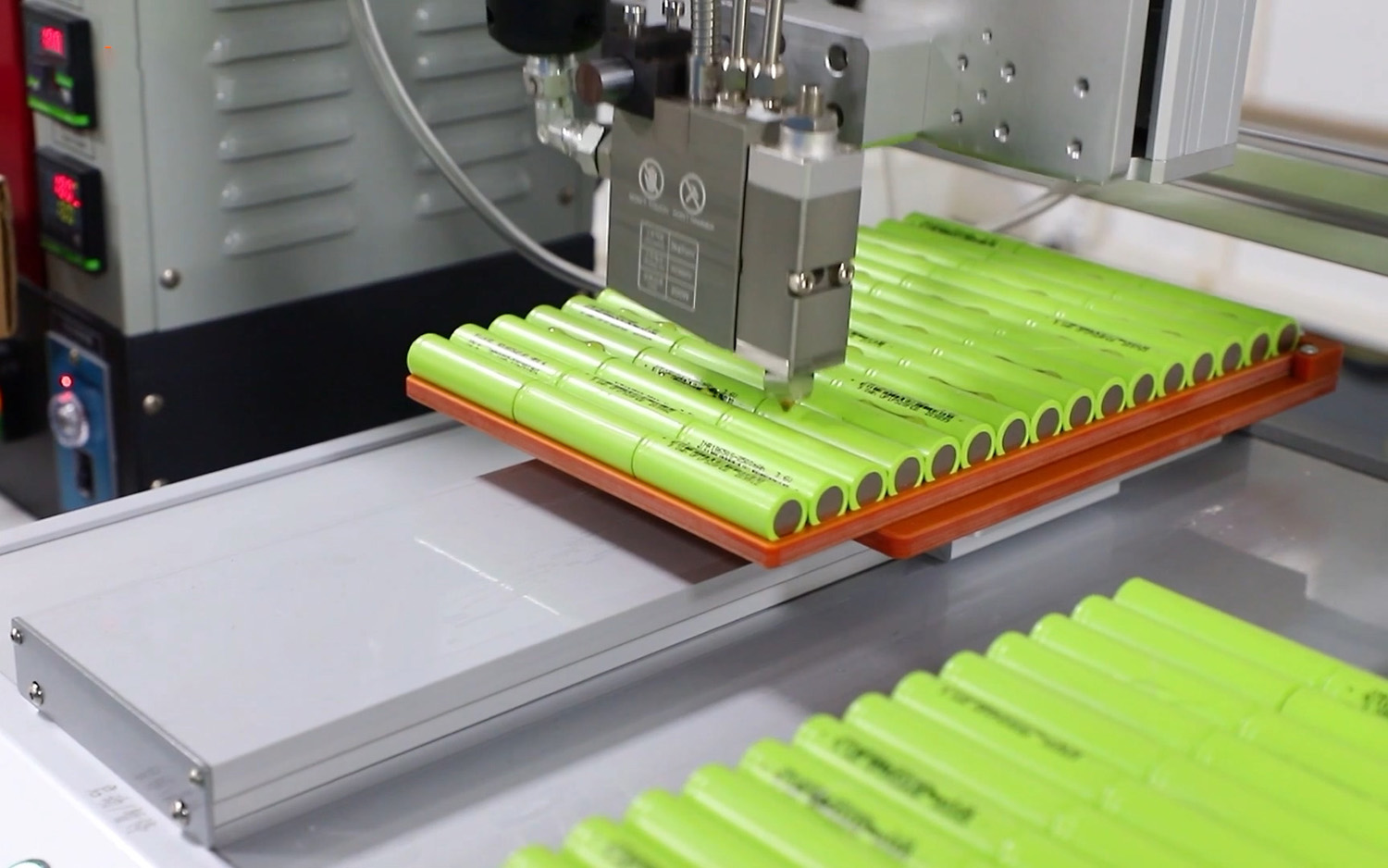
Batteries are the main power source of products, which can drive devices to operate. Detailed testing of batteries using testing tools can ensure the safety of batteries and prevent situations such as self-ignition and explosion due to high temperatures. Cars are our main means of transportation and are used frequently, so it is necessary to test batteries to ensure the safety of drivers. The testing method simulates various accident scenarios to determine whether the battery's quality is qualified and observe whether the battery will explode. By using these tests, risks can be effectively avoided and stability can be maintained.
1. Cycle Life
The number of cycles of a lithium battery reflects how many times the battery can be charged and discharged repeatedly. Depending on the environment in which the lithium battery is used, the cycle life can be tested to determine its performance at low, ambient, and high temperatures. Typically, the battery's abandonment criteria are selected based on its use. For power batteries (such as electric vehicles and forklifts), the discharge capacity maintenance rate of 80% is usually used as the standard for abandonment, while for energy storage and storage batteries, the discharge capacity maintenance rate can be relaxed to 60%. For the batteries we commonly encounter, if the discharged capacity/initial discharged capacity is less than 60%, it is not worth using as it won't last long.
2. Rate Capability
Nowadays, lithium batteries are not only used in 3C products but also increasingly used in power battery applications. Electric vehicles require changing currents under different operating conditions, and the demand for rapid charging of lithium batteries is increasing due to the shortage of charging stations. Therefore, it is necessary to test the rate capability of lithium batteries. Testing can be conducted according to the national standards for power batteries. Nowadays, battery manufacturers both domestically and internationally are producing special high-rate batteries to meet market needs. The design of high-rate batteries can be approached from the perspectives of active material types, electrode density, compaction density, tab selection, welding process, and assembly process. Those who are interested can find out more about it.
3. Safety Testing
Safety is a major concern for battery users. Incidents such as phone battery explosions or fires in electric vehicles can be terrifying. The safety of lithium batteries must be inspected. Safety testing includes overcharging, over-discharging, short circuit, dropping, heating, vibration, compression, piercing, and more. However, according to the perspective of the lithium battery industry, these safety tests are passive safety tests, meaning that batteries are exposed to external factors intentionally to test their safety. The design of the battery and module need to be appropriately adjusted for safety testing, but in actual use, such as when an electric vehicle crashes into another vehicle or object, irregular collisions may present more complex situations. However, this type of testing is more costly, so relatively reliable test content needs to be selected.
4. Discharge at Low and High Temperatures
Temperature directly affects the battery's discharge performance, reflected in the discharge capacity and discharge voltage. As the temperature decreases, the internal resistance of the battery increases, the electrochemical reaction slows down, the polarization resistance rapidly increases, and the battery's discharge capacity and voltage platform decrease, affecting the power and energy output.
For lithium-ion batteries, the discharge capacity sharply decreases under low-temperature conditions, but the discharge capacity under high-temperature conditions is not lower than that at ambient temperature; sometimes, it may even be slightly higher than the capacity at ambient temperature. This is mainly due to the faster migration of lithium ions at high temperatures and the fact that lithium electrodes, unlike nickel and hydrogen storage electrodes, do not decompose or produce hydrogen gas to reduce capacity at high temperatures. When discharging battery modules at low temperatures, heat is generated due to resistance and other factors, causing the battery temperature to rise, resulting in a voltage rise. As the discharge continues, the voltage gradually decreases.
Currently, the main battery types in the market are ternary batteries and lithium iron phosphate batteries. Ternary batteries are less stable due to structural collapse in high temperatures and have lower safety than lithium iron phosphate batteries. However, their energy density is higher than that of lithium iron phosphate batteries, so both systems are co-developing.
Post time: Sep-06-2023